PureDataの機能拡張をつくりたいなと思ってトライしたことがあるのですが、すっかり忘れてしまっていたのでメモしていきたいと思います。
Githubのpure-dataのリポジトリに、externals-howtoというものがあります。
https://github.com/pure-data/externals-howto
bangでメッセージを出力する
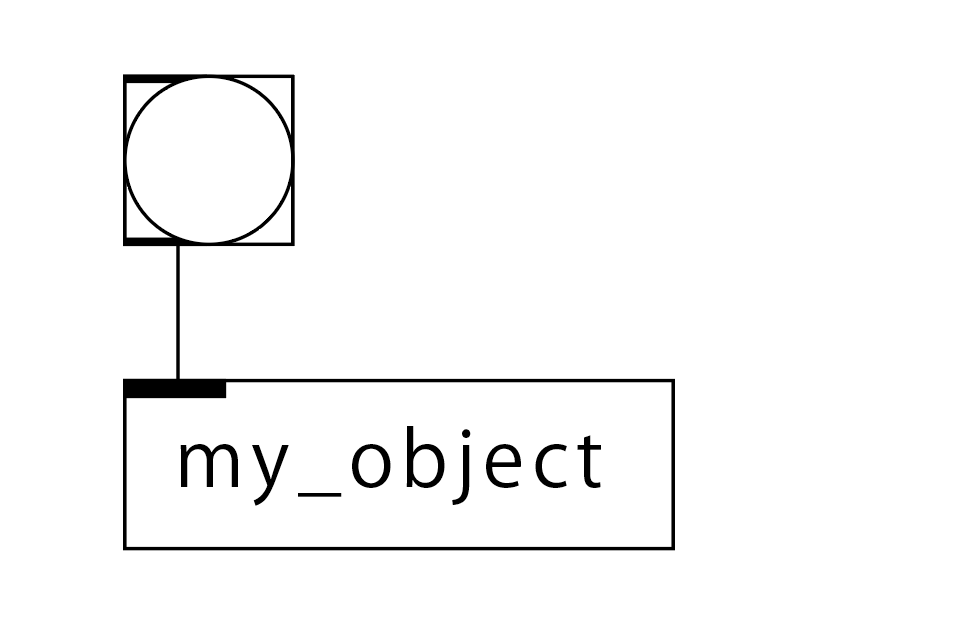
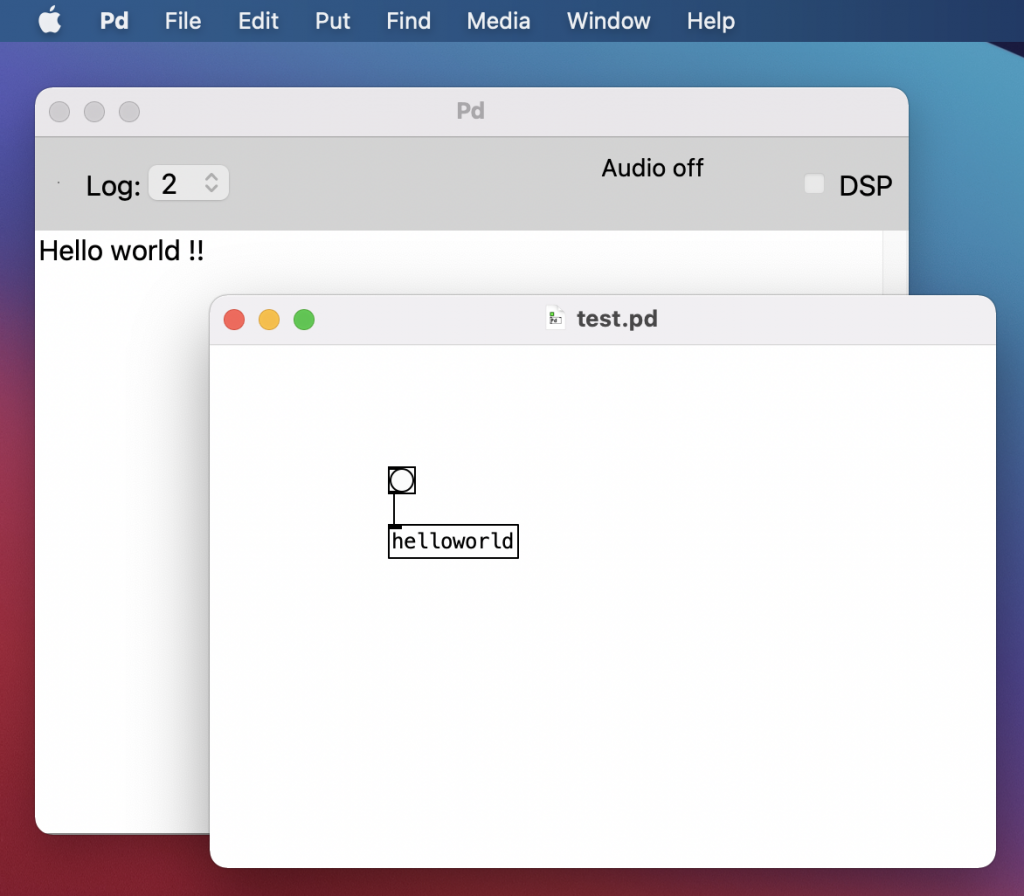
シンプルに、bangを受けとってPdウィンドウにメッセージを出力するオブジェクトの例。出力はメッセージで「Hello world !!」と出てきます。externals-howtoの中にある「example1」のソースがそれです。
/*
* HOWTO write an External for Pure data
* (c) 2001-2006 IOhannes m zm�lnig zmoelnig[AT]iem.at
*
* this is the source-code for the first example in the HOWTO
* it creates an object that prints "Hello world!" whenever it
* gets banged.
*
* for legal issues please see the file LICENSE.txt
*/
/**
* include the interface to Pd
*/
#include "m_pd.h"
/**
* define a new "class"
*/
static t_class *helloworld_class;
/**
* this is the dataspace of our new object
* we don't need to store anything,
* however the first (and only) entry in this struct
* is mandatory and of type "t_object"
*/
typedef struct _helloworld {
t_object x_obj;
} t_helloworld;
/**
* this method is called whenever a "bang" is sent to the object
* the name of this function is arbitrary and is registered to Pd in the
* helloworld_setup() routine
*/
void helloworld_bang(t_helloworld *x)
{
/*
* post() is Pd's version of printf()
* the string (which can be formatted like with printf()) will be
* output to wherever Pd thinks it has too (pd's console, the stderr...)
* it automatically adds a newline at the end of the string
*/
post("Hello world !!");
}
/**
* this is the "constructor" of the class
* this method is called whenever a new object of this class is created
* the name of this function is arbitrary and is registered to Pd in the
* helloworld_setup() routine
*/
void *helloworld_new(void)
{
/*
* call the "constructor" of the parent-class
* this will reserve enough memory to hold "t_helloworld"
*/
t_helloworld *x = (t_helloworld *)pd_new(helloworld_class);
/*
* return the pointer to the class - this is mandatory
* if you return "0", then the object-creation will fail
*/
return (void *)x;
}
/**
* define the function-space of the class
* within a single-object external the name of this function is special
*/
void helloworld_setup(void) {
/* create a new class */
helloworld_class = class_new(gensym("helloworld"), /* the object's name is "helloworld" */
(t_newmethod)helloworld_new, /* the object's constructor is "helloworld_new()" */
0, /* no special destructor */
sizeof(t_helloworld), /* the size of the data-space */
CLASS_DEFAULT, /* a normal pd object */
0); /* no creation arguments */
/* attach functions to messages */
/* here we bind the "helloworld_bang()" function to the class "helloworld_class" -
* it will be called whenever a bang is received
*/
class_addbang(helloworld_class, helloworld_bang);
}
プログラムのポイント
Pdのオブジェクトの場合、入力のインレットと出力のアウトレットがあり、何か受け取ると、その結果を吐き出す、という動きをします。そこで、プログラムのポイントとなろのは、「インレットをつくる」「アウトレットをつくる」ところです。
そしてやりとりするものには、いくつか種類があり、その種類ごとにプログラムの書き方が異なります。なので、まずは、ひとつずつの書き方をみていきます。
- bang
- 小数
- シンボル
- 信号 など
void helloworld_setup(void)
setup関数の中では、オブジェクトの名前と、bangのインレットを定義しています。
オブジェクトの名前
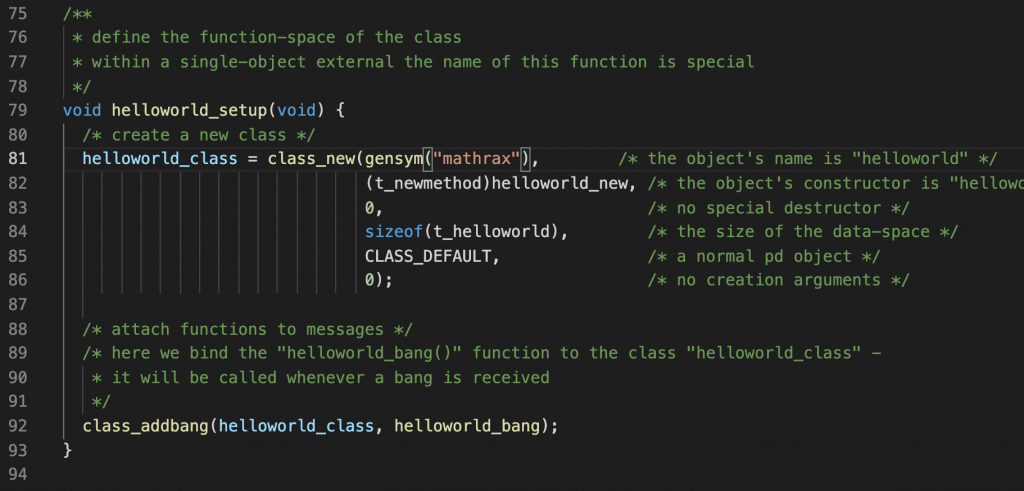
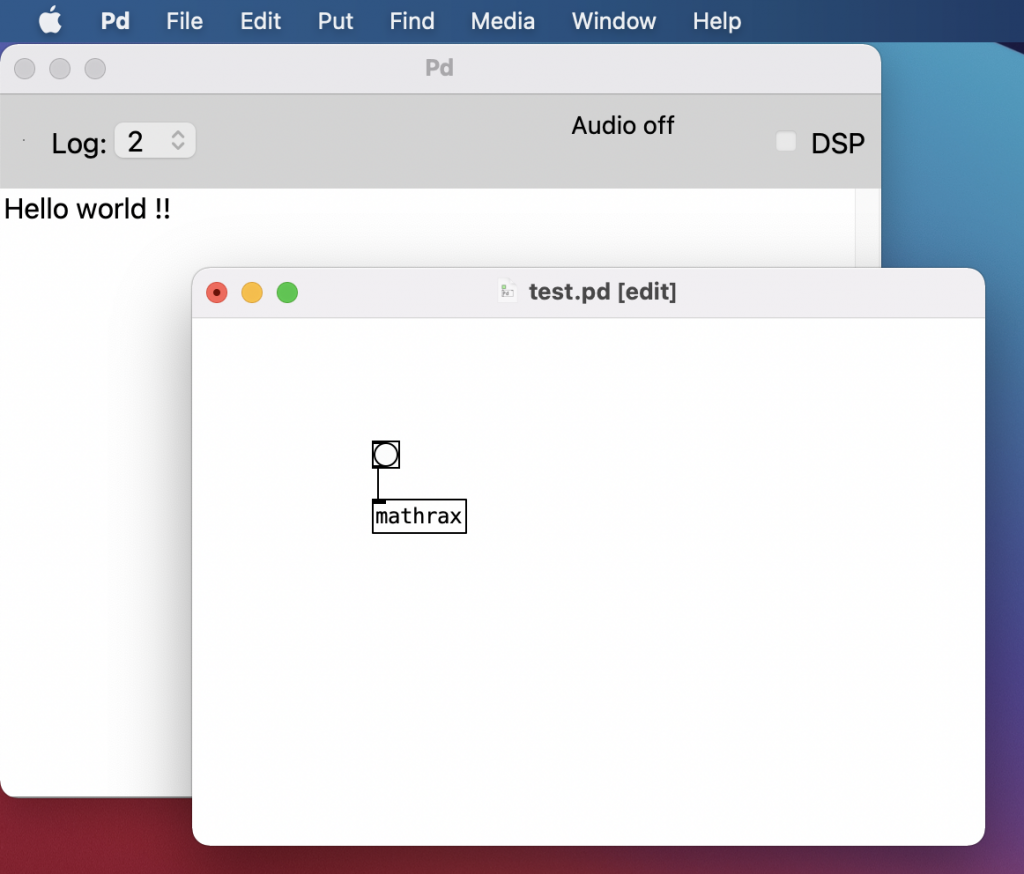
81行目の「helloworld」を「mathrax」に変えてみると、オブジェクトの名前が変えることができます。ソースの中にある名前や、MakeFileの中にある名前は関係ないことがわかりました。でも、混乱するので、理解できてきたら全部変更しておくとよいと思います。
bangのインレット
class_addbang(helloworld_class, helloworld_bang);
92行目の「class_addbang」というところで、先ほど名前を定義したオブジェクト「helloworld_class」に、bangが入力されたときに実行する「helloworld_bang」関数を追加しています。
/**
* this method is called whenever a "bang" is sent to the object
* the name of this function is arbitrary and is registered to Pd in the
* helloworld_setup() routine
*/
void helloworld_bang(t_helloworld *x)
{
/*
* post() is Pd's version of printf()
* the string (which can be formatted like with printf()) will be
* output to wherever Pd thinks it has too (pd's console, the stderr...)
* it automatically adds a newline at the end of the string
*/
post("Hello world !!");
}
「helloworld_bang」関数では、「post」という命令をつかってPdウィンドウにメッセージを「Hello world !!」とメッセージを表示しています。
void *helloworld_new(void)
オブジェクトの初期化
順番が前後しますが、オブジェクトの名前を決めたところで、Pdで実際にオブジェクトを生成したときに初期化する関数を定義しています。
/**
* define the function-space of the class
* within a single-object external the name of this function is special
*/
void helloworld_setup(void) {
/* create a new class */
helloworld_class = class_new(gensym("helloworld"), /* the object's name is "helloworld" */
(t_newmethod)helloworld_new, /* the object's constructor is "helloworld_new()" */
0, /* no special destructor */
sizeof(t_helloworld), /* the size of the data-space */
CLASS_DEFAULT, /* a normal pd object */
0); /* no creation arguments */
/* attach functions to messages */
/* here we bind the "helloworld_bang()" function to the class "helloworld_class" -
* it will be called whenever a bang is received
*/
class_addbang(helloworld_class, helloworld_bang);
}
実際の「helloworld_new」関数を見てみると、「x」という変数にオブジェクトを格納して返しているようです。
/**
* this is the "constructor" of the class
* this method is called whenever a new object of this class is created
* the name of this function is arbitrary and is registered to Pd in the
* helloworld_setup() routine
*/
void *helloworld_new(void)
{
/*
* call the "constructor" of the parent-class
* this will reserve enough memory to hold "t_helloworld"
*/
t_helloworld *x = (t_helloworld *)pd_new(helloworld_class);
/*
* return the pointer to the class - this is mandatory
* if you return "0", then the object-creation will fail
*/
return (void *)x;
}
次は、bangを受けると、数をカウントしながら出力する「counter」というオブジェクトを作ってみます。
